Describe Some of the Uses and Drawbacks of Raman Spectroscopy
Atomic and infrared spectroscopy which have. Raman spectroscopy in contrast can detect homonuclear molecules but it has very low sensitivity.

Applications For Raman Spectroscopy In Biomedicine Download Scientific Diagram
If the Raman bands change on the screen within a second or two from the start of the analysis it is likely that the specimen is being adversely affected by the laser beam.

. Keywords Optical biosensors Surface enhanced Raman scattering SERS Cancer Optofluidics Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy 1 Introduction Human cancer is a complex disease commonly induced by. Raman spectroscopy ˈ r ɑː m ən. These disadvantages make it challenging to use conventional Raman spectroscopy for practical applications involving biological detection.
Pitfalls and drawbacks Fluorescence The laser beam can excite electronic transitions that may mask the Raman signal. We will discuss how characteristics such as disorder edge and grain boundaries thickness doping strain and thermal conductivity of graphene can be learned from Raman spectroscopy. However the scattered light intensity of Raman scattering is typically extremely weak 17 and auto-fluorescence is often present in biological samples making the detection of Raman signals difficult 24.
Spectroscopy also provides a precise analytical method for finding the constituents in material having. As such Raman spectroscopy was born. There are many categories of spectroscopy eg.
However we believe there are some problems that need to be considered. First there is insufficient evidence that Raman spectroscopy can be used to measure changes in the. Both near-IR absorption and Raman spectroscopy need special enhancement techniques to be useful in gas-phase analysis.
Brief discussion of some of the emerging challenges in the field and some of the approaches that are likely to enhance their application. The only exception is pure metals which just reflect light. Raman spectroscopy applications include reaction monitoring and the verification and identification of substances including illegal and hazardous materials.
Raman is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Altangerel et al. Through specific spectral patterns substances can be identified and molecular changes can be observed with high.
Two studies are highlighted to demonstrate basic science and. One of the most useful applications of light scattering spectroscopy is Raman spectroscopy. Recently two new techniques were introduced for sensitive.
As a vibrational spectroscopy technique it is complementary to the also well-established infrared spectroscopy. Material characterization Pharmaceutical analysis. Once the Raman effect was discovered there was no doubt that an opportunity had arisen to make use of the effect as an analytical tool.
RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY OF GRAPHENE. Raman spectroscopy has become a powerful noninvasive method to characterize graphene and related materials 8. However metallurgists use Raman spectroscopy because carbides nitrides and oxides do Raman scatter.
Raman spectra can generally be measured from solids liquids and gases including thin films and powders. Analysis of some sample involves monochromatic light from a laser in the visible near infrared or near UV range λ 350-1000 nm interacting with the phonons quantized. Spatially offset Raman spectroscopy SORS is a spectroscopic technique that allows for the non-invasive chemical characterization of diffusely scattering materials ranging from opaque plastics.
It uses light Scientists and engineers can apply the tricks they already know about manipulating light to Raman spectroscopy. Measurements through packaging make it a very safe technique for authorities such as the police first-responders and customs but also for warehouse personnel working as incoming goods inspectors. If any Raman peaks are visible at all they.
Named after Indian physicist C. Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of energy levels in atoms or molecules using absorbed or emitted electromagnetic radiation. The large number of wavelengths emitted by these systems makes it possible to investigate their structures in detail including the electron configurations of ground and various excited states.
Fitting a powerful microscope to a Raman spectrometer enables. Up to 24 cash back Scattering spectroscopy measures the amount of light that a substance scatters at certain wavelengths incident angles and polarization angles. Applications of Raman Spectroscopy to Earth Sciences and cultural Heritage.
The scattering process is much faster than the absorptionemission process. Raman Spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy has become an incredibly useful analytical technique for the identification of organic inorganic and biological samples. Raman spectroscopy is an emerging analytical approach that probes the molecular signature of endogenous cellular biomolecules under biocompatible conditions with high spatial resolution.
Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which. IR Versus Raman -. Over the last decade Raman spectroscopy has gained more and more interest in research as well as in clinical laboratories.
1 suggest that Raman spectroscopy can be used to detect the early abiotic stress response in plants through the measurement of anthocyanins and carotenoids in plant tissues. Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay paper or report. Raman spectroscopy has been used to support formulation development with applications in aggregation particulates and real-time release of formulation buffers 8789.
Instead the incident light will excite the system to a high-energy state. However in Raman spectroscopy UV VIS or NIR light is used as radiation source which has a much higher energy than those energy differences and absorption of photons is impossible. Spectroscopy is used as a tool for studying the structures of atoms and molecules.
Spectroscopy also finds uses in astronomy to obtain information about the composition density temperature and other principal physical processes of a certain astronomical object. 14 -16 th of june 2012 Perfect Hermite Gaussian laser beam θ0 0 0 2 0 0 θ θ w w M R R The quality factor M 2 called the M-squared factor is defined to describe the deviation of the laser beam from a theoretical. Typically provide detection limits that are of little practical use.
Applications of Raman spectroscopy in prostate cancer include biopsy analysis assessment of surgical margins and monitoring of treatment efficacy.

Benefits And Uses Of Using Raman Spectrometer Jockey P2p

Raman Spectroscopy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Raman Spectroscopy Hamamatsu Photonics

Schematic Of Raman Spectrometer The Displayed Set Up Focuses The Download Scientific Diagram

Raman Spectroscopy Applications Anton Paar Wiki

Instrument Presentation Horiba
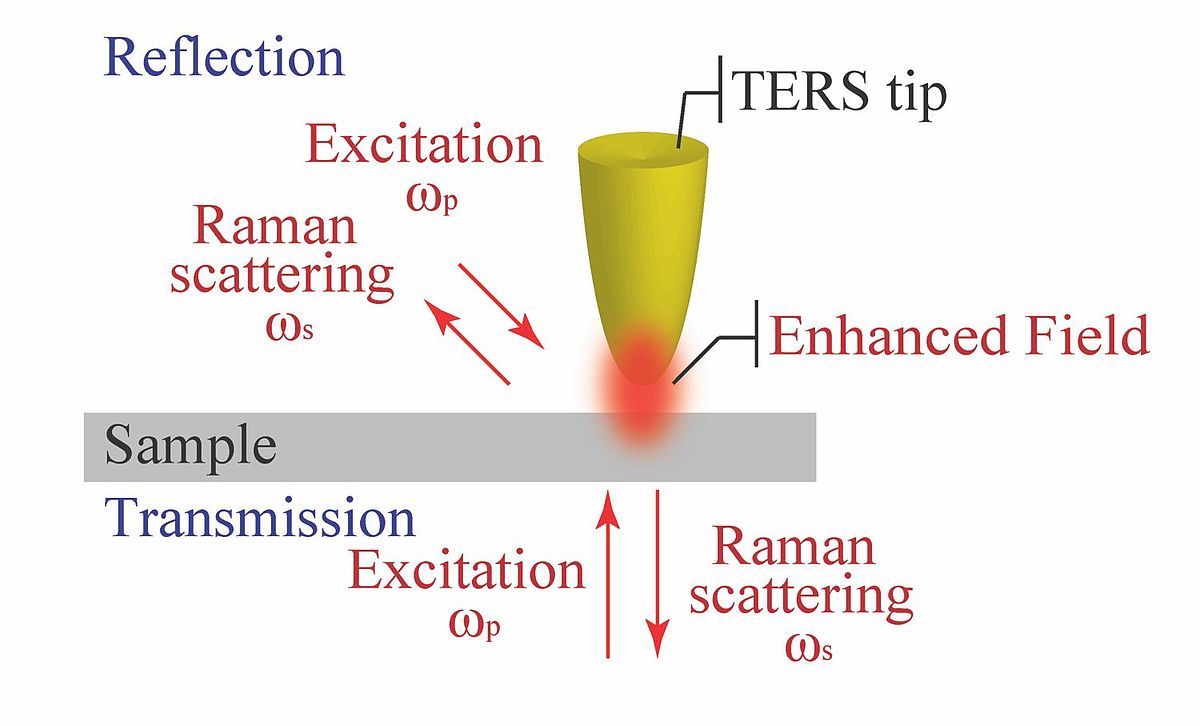
What Is Tip Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Horiba

What Is Raman Spectroscopy Horiba

What Is Raman Spectroscopy Horiba

Raman Spectroscopy Applications Anton Paar Wiki
Raman Spectroscopy An Evolving Technique For Live Cell Studies Analyst Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C6an00152a

Basics And Principle Of Raman Spectroscopy Learn Under 5 Min Stokes And Anti Stokes Ai 09 Youtube

Theory Of Raman Effect A Interpretation Of Raman Scattering Via Download Scientific Diagram
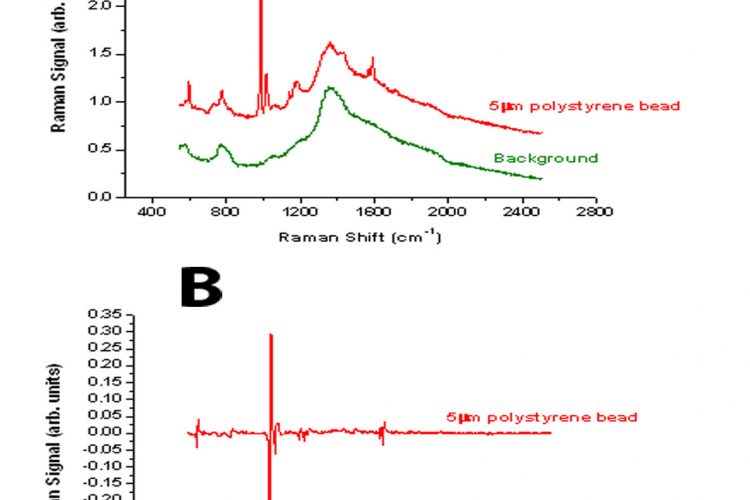
Raman Spectroscopy And Cancer Cells European Pharmaceutical Review
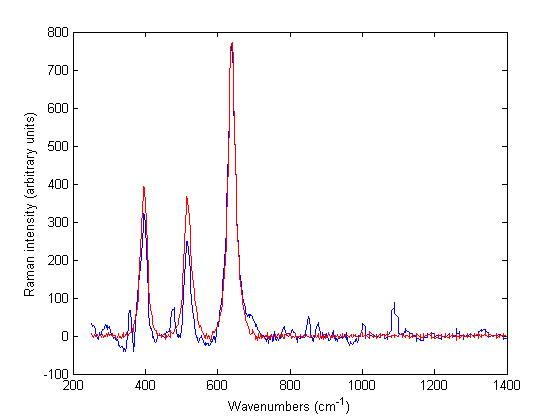
Authentication Of Medicines Using Raman Spectroscopy European Pharmaceutical Review
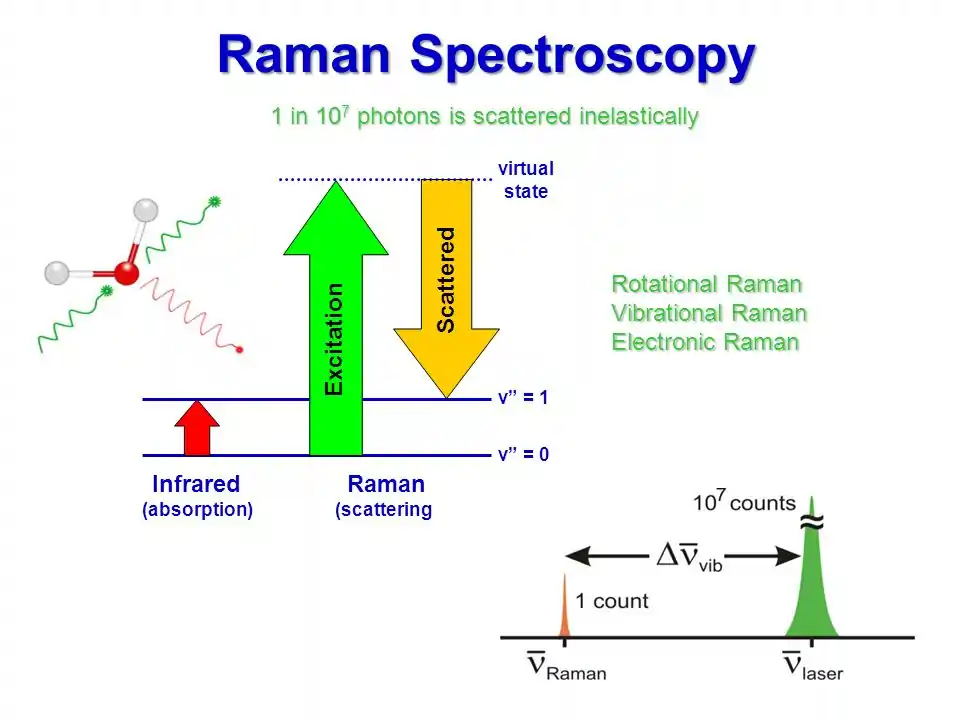
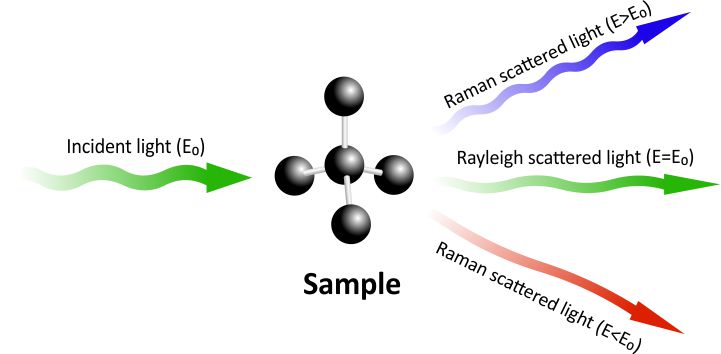

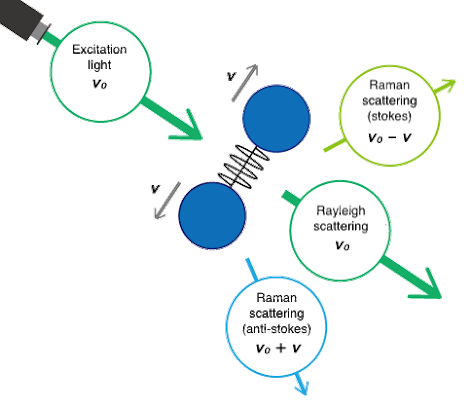
Comments
Post a Comment